What Are The Functions Of The Organelles In An Animal Cell?
Definition of organelle
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The cellular components responsible for the functioning of a cell are called cell organelles. Different organelles present within the jail cell are classified into three categories based on the presence or absence of the membrane.
- Organelles without membrane: include prison cell wall, ribosomes and cytoskeleton. These organelles are present in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
- Single membrane bound organelles: include vacuole, Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum and lysosome and are present simply in eukaryotic cells.
- Double membrane leap organelles: include nucleus, chloroplast and mitochondria. These organelles are nowadays only in eukaryotic cells.
These organelles as well differ in their structures and functions performed past them. For normal functioning of the cells, these organelles coordinate and office efficiently. Few organelles part by providing shape and support whereas some are responsible for locomotion and reproduction of the cell.
Besides Read:Chromosome
Types of organelles and their functions
[Click Hither for Sample Questions]
Beneath are listed the types of organelles with their functions.
Prison cell Membrane
Cell membrane is also called plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane. It is present in both animal and institute cells. Cell membrane is composed of lipid bilayer and proteins. Plasma membrane is a selectively permeable membrane i.due east., it permits the entry of selective material inside and outside of the cell depending on the requirement. The function of the cell membrane is that it provides shape and protects the internal content of the cell. Model for plasma membrane was proposed called a fluid mosaic model. According to this model, the lateral move of proteins within the overall bilayer is due to the quasi-fluid nature of lipids and this power to move within the membrane is measured as fluidity.
Jail cell Wall
Prison cell wall is a non-living structure forming the outer roofing for the plasma membrane of fungi and plants. Cell wall gives shape to the cell and protects the prison cell from damage and infection. Information technology also helps in prison cell-to-cell interaction and provides a bulwark to undesirable macromolecules. The cell wall of algae is equanimous of cellulose, galactans, mannans and minerals similar calcium carbonate. And the cell wall of plants has a composition of cellulose, hemicellulose, pectin and proteins. The cell wall of young plants is capable of growth which is gradually diminished while the prison cell matures and then forms the secondary wall on the inner side of the prison cell. The middle lamella layer mainly consists of calcium pectate which holds dissimilar neighbouring cells together. The jail cell wall and middle lamellae may be traversed by plasmodesmata connecting the cytoplasm of neighbouring cells.
Cytoplasm
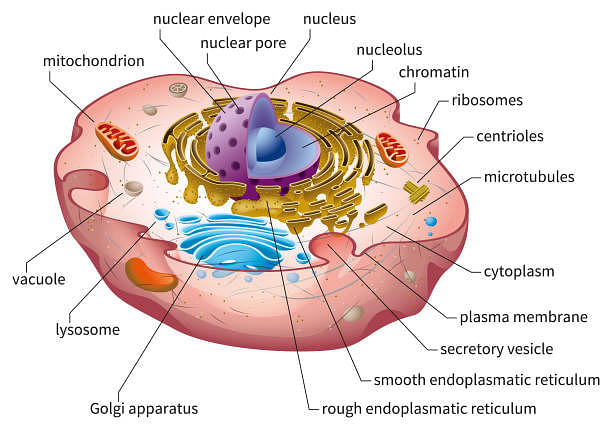
Cytoplasm Structure
Cytoplasm is a jelly-like substance found between cell membrane and nucleus. All the jail cell organelles are embedded in the cytoplasm. It is composed of water, organic and inorganic compounds. Cytoplasm is one of the essential components of the prison cell that is nowadays in both plant and creature cells. Cytoplasm functions past controlling all the metabolic activities taking identify within the cell and most of the chemic reactions are carried inside it.
Also Read: Difference Between Cytoplasm and Protoplasm
Nucleus
Nucleus is a double membraned and the largest organelle present in all eukaryotic cells. It acts as the storehouse of the cell`s DNA and functions as the command middle of the cellular activities. This round nucleus is surrounded by a nuclear membrane and is dark in colour. The nuclear membrane is a porous membrane and forms a wall between cytoplasm and nucleus. Nucleus contains tiny spherical bodies called nucleolus. It also carries other essential construction called chromosomes. Chromosomes are a thread similar structures which conduct other important component called factor.
Gene is a hereditary unit of measurement of organisms that helps transfer traits from parents to offspring. Therefore, nucleus controls the functions and characters of the cell in organisms. The chief function of the nucleus is to monitor cellular activities including metabolism and growth. Protein and RNA is also synthesized in the nucleus with the help of nucleoli.
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic reticulum is a network of tiny tubular structures scattered in the cytoplasm. It divides the intracellular space into two distinct compartments, one is luminal (within ER) and some other is actress luminal (outside ER). They office as the send system of a cell, involved in transporting materials throughout the cell.
Endoplasmic reticulum is divided into two types based on presence and absence of ribosomes.
- Rough endoplasmic reticulum: The endoplasmic reticulum bearing ribosomes on their surface is called rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER). Information technology is involved in the poly peptide synthesis and secretion. They are all-encompassing and continuous with the outer membrane of the nucleus.
- Smooth endoplasmic reticulum: The endoplasmic reticulum with the absence of ribosomes on its surface is chosen smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). They are responsible for lipid syntheses. In animal cells, lipid similar steroid hormones is synthesized in SER. They are too responsible for detoxifying the prison cell.
Mitochondria
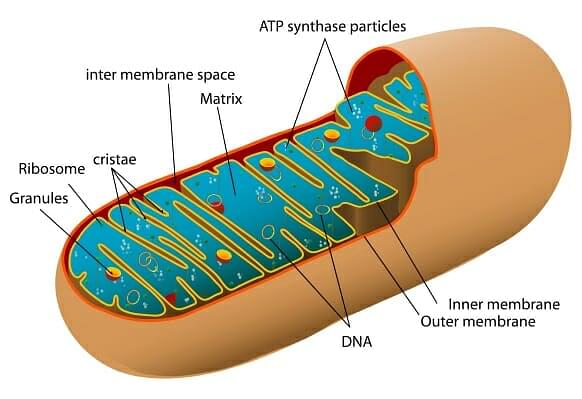
Mitochondria
Mitochondrion is a double membrane jump jail cell organelle that are not normally visible nether the microscope. This cylindrical or sausage shaped construction is also chosen the power house of the cell every bit they are the sites for aerobic respiration of the prison cell and produce cellular free energy in the form of ATP. The outer membrane and the inner membrane divide its lumen into two compartments i.east., inner compartment chosen matrix possessing single round Deoxyribonucleic acid molecule and a few RNA molecules. forming a number of infoldings called cristae and the outer membrane forming the continuous limiting purlieus of the organelle. Depending on the shape, size and physiological activity of the prison cell, the number of mitochondria per cell are variable. The structure has a diameter of 0.2 to 1µm (boilerplate 0.v µm) and length 1.0 to 4.i µm.
Likewise Read: Divergence Betwixt Mitochondria and Chloroplast
Plastids
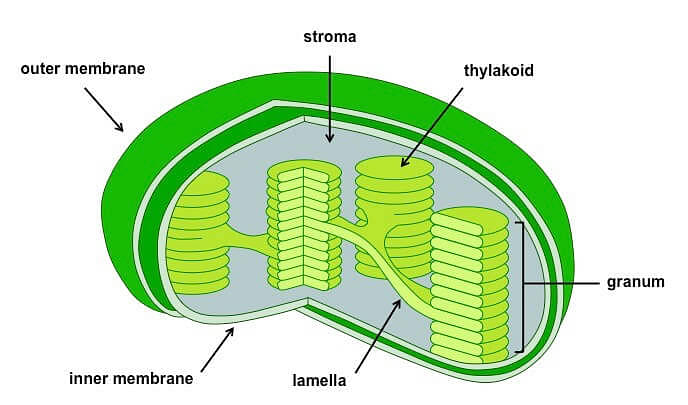
Plastids
Plastids are large and membrane spring organelles that are found in all plants and in euglenoids. They contain some specific pigments that are responsible for imparting specific colours to the plants. On the basis of the type of paint, plastids can be classified into three types.
- Chloroplasts: Chloroplasts are double membrane bound jail cell organelles that incorporate chlorophyll and carotenoid pigments that are responsible for trapping calorie-free energy and this energy is used for the purpose of photosynthesis.
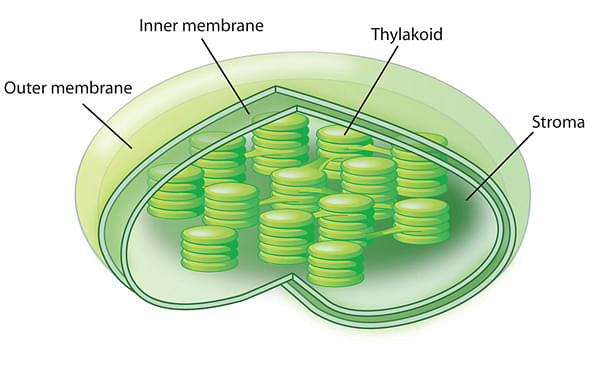
Chloroplasts
The inner membrane surrounds a infinite called stroma. Chlorophyll containing structures chosen thylakoids are arranged as piles of coins and each pile is called a granum. Thylakoids are connected past flat membranous tubules known equally stromal lamella.
- Chromoplasts: These include carotenoid, fat soluble pigments like carotene, xanthophyll etc. providing characteristic colours like yellow, orange, red, etc. to the plants.
- Leucoplasts: These types of plastids store nutrients and are colourless. They include amyloplasts storing carbohydrates, aleuroplasts storing proteins, and elaioplasts storing oils and fats.
Besides Read:
Ribosomes
Ribosomes are dumbo particles with granular structures. They have a composition of 2/3 of ribonucleic acid (RNA) and ane/3 of proteins. They are not surrounded by any membrane. Ribosomes present in eukaryotic cells is 80S while ribosomes found in prokaryotes is 70S. The letter South represents the density and size and is chosen Svedberg`south unit. Both 70S and 80S ribosomes are equanimous of two subunits. The master function of the ribosomes is protein synthesis in all living cells ensuring the survival of the cell.
Likewise Read: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Cytoskeleton
Cytoskeleton is a network of filamentous proteinaceous structures present in the cytoplasm. The functions of cytoskeleton include move, mechanical support and maintenance of the shape of the cell.
Golgi apparatus
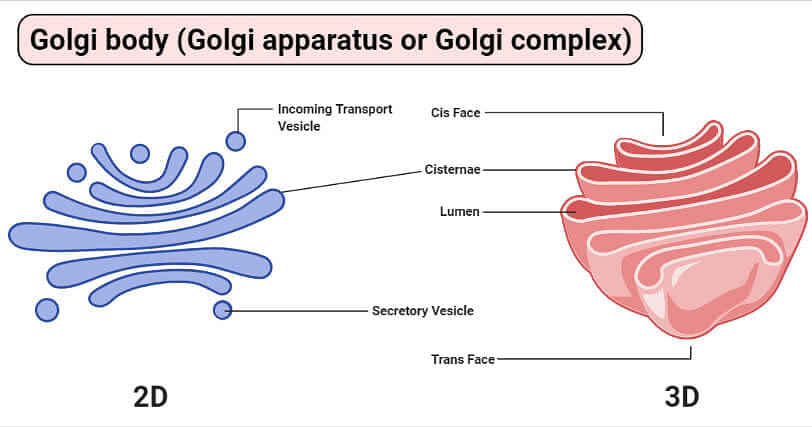
Golgi apparatus
Golgi apparatus is a membrane jump organelle composed of flattened, stacked pouches called cisternae. It is also chosen the Golgi complex. Golgi apparatus is responsible for transporting, modifying, and packaging proteins and lipids to their targeted destinations. These are institute in both plant and animal cells.
Microbodies
Microbodies are the membrane bound infinitesimal vesicles that comprise various enzymes. They are plant in both found and brute cells. They can be visualised just under the electron microscope.
Cilia and flagella
The hair-like outgrowths or projections of the cell membrane are called cilia (sing: cilium). They work like oars to motion either the prison cell or the outside fluid. On the other paw, flagella are bigger than cilia and are responsible for cell movements. Flagella possessed by prokaryotic bacteria are structurally different from that of eukaryotic flagella.
Both cilia and flagella are covered with plasma membranes. The core of the cilium and flagellum is known equally axoneme containing nine pairs of peripheral microtubules and a set of central microtubules running parallel to the axis. This arrangement of axonemal microtubules is called a 9+ii array. The central tubules are connected past bridges and are too embedded by a central sheath that is continued to i of the tubules of each peripheral doublets by a radial spoke. Thus, there are nine radial spokes. Both the cilium and flagellum sally from centriole-similar structures called the basal bodies.
Centrosome and centrioles
Centrosome is a structure formed by 2 mutually perpendicular structures known equally centrioles. Centriole consists of every bit spaced ix peripheral fibrils of tubulin poly peptide. Core part of the centriole is proteinaceous and is known as a hub. Information technology connects the fibrils through radial spokes made of proteins. During the cell partition, centrioles from the basal bodies of cilia and flagella give rise to spindle fibres.
Vacuoles
Vacuoles are defined every bit storage bubbling of irregular shapes and fluid filled organelles enclosed past membranes. They are responsible for storage of the nutrient or nutrients that are needed by a cell. They as well store waste products and these waste matter products are eventually thrown out past vacuoles. So, because of the presence of vacuoles, the cell is protected from contamination. Institute cells have larger vacuoles as compared to animal cells.
Too Read: Deviation Between Cell and Tissue
Things to call up
- Organelles are the cellular components responsible for the normal functioning of the cell.
- Organelles are classified into three types i.e., organelles without membrane, single membrane leap organelle and double membrane bound organelle.
- Fluidity is the mensurate of the movement of the proteins inside the membrane.
- Cytoplasm is responsible for decision-making all the metabolic action of the jail cell.
- Nucleus is the largest organelle institute inside the cell and is considered equally the control middle of the cell.
- Nucleus contains thread-like structures chosen chromosomes and some other construction called a gene which is responsible for transfer of traits from parents to offspring.
- Nucleus is also responsible for cell division.
- Endoplasmic reticulum is the transport system of the cell. Crude endoplasmic reticulum and shine endoplasmic reticulum are the ii types of endoplasmic reticulum.
- Mitochondria is considered as the site for aerobic respiration in the cell and information technology produces energy in the form of ATP and is given a second proper noun every bit ability house of the cell.
- Plastids are of 3 types, Chloroplasts, chromoplasts and leucoplasts. Chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis in the plants.
- Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis in all living cells that ensure the survival of the cell.
- Golgi apparatus is responsible for transporting, modifying, and packaging proteins and lipids to targeted destinations.
- Cytoskeleton provides shape and mechanical support to the cell.
- Cilia and flagella are responsible for the movement of the cell.
- Vacuoles store food or different nutrients needed by the cell.
Sample questions
Ques. Why are lysosomes known equally suicide bags? (ii Marks)
Ans. Lysosomes are capable of breaking down all the wastes, damaged and expressionless cells. That is why lysosomes are called suicide numberless.
Ques. What is cell organelle and what are the functions of cell organelles? (two Marks)
Ans. Jail cell organelles are the compartments within the cells performing different functions. These organelles are divided into three types i.e., organelles without membrane, single membrane spring organelle and double membrane bound organelle. The examples of organelles are mitochondria, plastids, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, etc.
Different organelles perform different functions in gild to proceed the jail cell live and safe. Some of The functions of the organelles include.
- Storage of food or nutrients that are required past cells. This part is carried out by vacuoles.
- Digestion of food particles and waste materials is done by lysosomes.
- ATP generation and aerobic respiration in cells is the office of mitochondria.
- Command and regulation
Ques. Which prison cell organelle stores nutrient? (2 Marks)
Ans. Vacuoles are the jail cell organelles that store food or different nutrients required for the cell.
Ques. What is a nucleoid? (two Marks)
Ans. Nucleoid is an irregularly shaped structure that contains most of the genetic cloth of a prokaryotic cell.
Ques. Where do we find chromoplast and chloroplast pigments in the cell? (2 Marks)
Ans. Chromoplast and the chloroplast are the pigments present in the plastid organelle of the prison cell.
Ques. Which cell organelle is called the powerhouse of the cell? (2 Marks)
Ans. Mitochondria is called the powerhouse of the cell.
Ques. Describe the structure of the nucleus? (2 Marks)
Ans. Nucleus is completely spring by membranes and is engaged by a construction called the nuclear envelope. Nucleus contains genetic materials of the cell known as chromosomes. DNA is present inside the chromosomes which provide genetic information for division of cells and creation of unlike cell components.
Ques. What is a centromere? (2 Marks)
Ans. Centromere is a specialised DNA sequence of a chromosome. The part of the centromere is the zipper of sister chromatids and spindle fibres. They are likewise responsible for segregation and proper alignment of chromosomes during process of cell segmentation in eukaryotic cells.
Related Links:
Source: https://collegedunia.com/exams/cell-organelles-definition-types-and-their-functions-biology-articleid-1668
Posted by: brownefolisn.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Are The Functions Of The Organelles In An Animal Cell?"
Post a Comment