What Is Dried Animal Manure Used For?
Download Resource
Animal manures and beast manure-based composts are rich in plant nutrients such equally Nitrogen (N), Phosphorous (P) and Potassium (K) and provide organic matter that conditions the soil. While they tin make splendid soil amendments for the home gardener, it is of import to use them effectively and safely.
Manure or Compost?
In that location are no regulations or standards in New Hampshire that govern the many labels that can exist used to describe soil amendments ("manure", "aged manure", "rotted manure", "composted", etc.). For the purposes of this fact sheet, "compost" refers to whatever mix of organic materials that has been partially decomposed to the signal where its nutrient content is stable. This typically implies an active process, where the organic materials are managed advisedly to speed decomposition. "Manure" refers to waste material from livestock (including poultry, cattle, or horses), usually mixed with bedding such equally sawdust or wood shavings and/or feed waste. Manures may be fresh – that is, they have non decomposed at all, or they may have decomposed (or "aged") to varying degrees.
Nutrient Content
Generally, institute nutrients in manures and composts are measured in terms of pounds per wet ton; it takes a lot of these materials to provide enough nutrients for plant growth. Food content varies widely depending on the type of manure and the amount and blazon of bedding in it, and the ingredients in compost. While gardeners tin use some full general guidelines for food content (see table below), the most accurate way to decide fertilizer equivalency is to have the cloth tested.
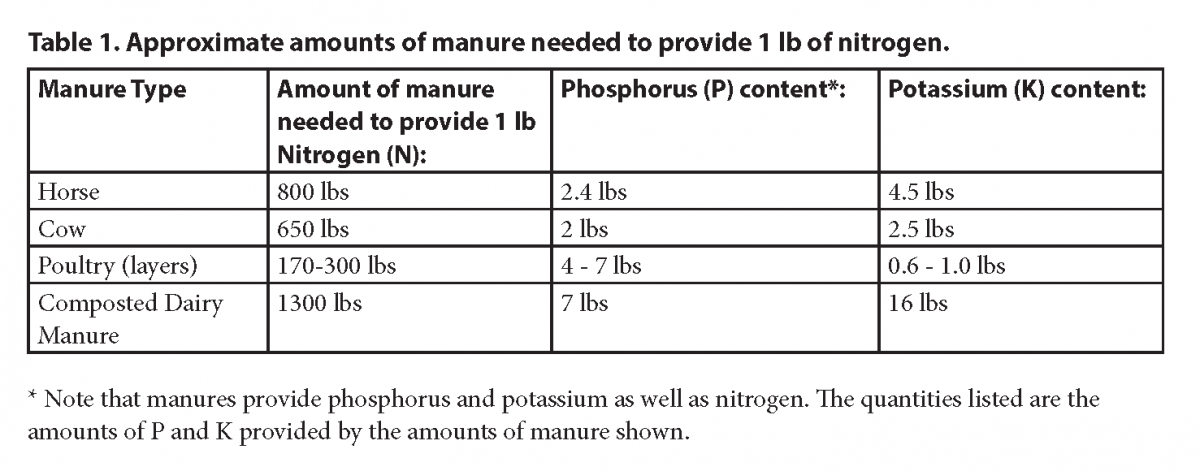
While most of the nutrients in manures and composts behave similarly in the soil to nutrients from commercial fertilizers, nitrogen is an exception. Showtime, much of the nitrogen is not immediately available to plants, but instead becomes bachelor slowly, as microbes digest information technology. Likewise, the availability of nitrogen depends on the ratio of carbon to nitrogen (C:Northward ratio). If the ratio exceeds 30:1, then near of the nitrogen is immobilized, or unavailable to plants, for an extended period. Manures or unfinished composts that contain a high proportion of bedding similar wood shavings or sawdust have a loftier C:N ratio. This type of material "borrows" nitrogen from the soil every bit information technology decomposes, and the result is that garden plants may non have the nitrogen they need to abound.
Environmental Concerns
The proportions of plant nutrients in composts and manures are commonly dissimilar from what plants crave for growth. In detail, these materials ofttimes incorporate more than phosphorus than nitrogen. Thus, gardeners that apply enough of these materials to meet nitrogen needs for their gardens will probable apply far more phosphorus than is needed. Over time, this tin can lead to very high levels of soil phosphorus.
What'due south the problem with high phosphorus? Very loftier soil phosphorus is not toxic, and volition non damage plants or people, only when phosphorus moves into surface waters, it can pb to algae blooms, which harm water quality and aquatic organisms.
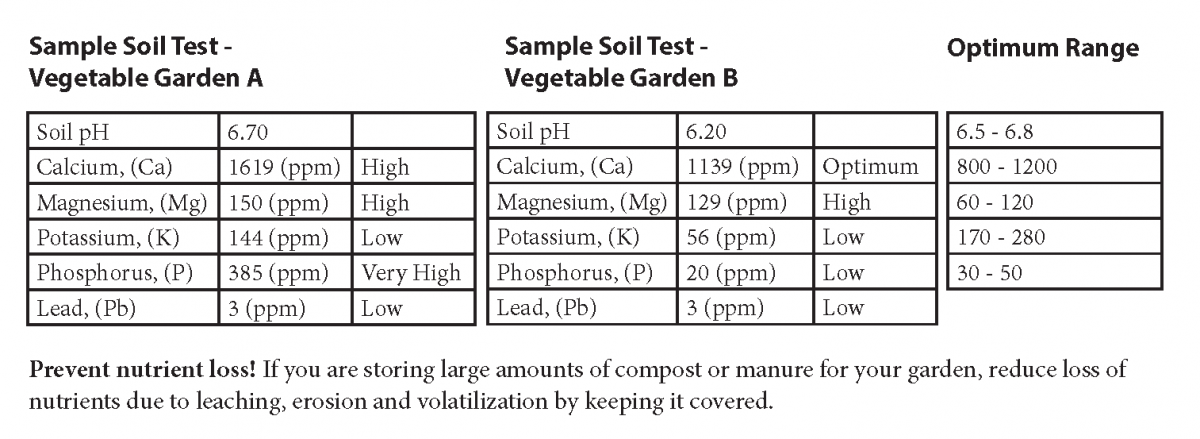
In order to use manures and composts effectively and responsibly, outset with testing your soil for pH and soil food status. If soil phosphorus is in the low to optimum range (upwards to 50 ppm on the University of New Hampshire (UNH) soil examination), feel free to use manure or compost to provide nutrients. If soil phosphorus examination levels are very high (over 100 ppm on UNH'southward soil test), consider using food sources other than manure.
In the soil test examples beneath, Garden A has very high levels of phosphorus, because of a history of compost applications. While nitrogen and potassium fertilizers are still needed for crops in this garden, this gardener should not add together more compost or manure, to avert becoming a source of phosphorus contamination. In contrast, Garden B has probably had very little or no compost or manure added to it, since the soil phosphorus levels are quite low. In this case, the gardener could add composts or manures to provide nutrients and organic affair.
Food Safety
For all the benefits of using manure and manure-based composts in the garden, in that location are also some risks. Animal manures harbor pathogens harmful to humans, including E. coli, Salmonella, and Campylobacter leaner, and Giardia or Cryptosporidium protozoa. These organisms can affect people when they eat crops contaminated with soil, and under certain weather, they can exist taken upwardly into plant tissue.
The risk from pathogens is greatly reduced when manure is composted correctly. To ensure that pathogens have been killed, the compost pile must reach a high temperature (between 131°F and 140°F) for a sustained period of time (several weeks). The compost must also be turned regularly and carefully monitored then that all of the manure has been exposed to sufficient temperatures. In dwelling house compost piles and in unmanaged manure piles, this rarely happens. Aged manure is not the same as composted manure, and it is not safe to assume that pathogens in an anile manure pile accept been destroyed.
Some other strategy for destroying pathogens is pasteurization. Some commercial poultry manure products are processed in this style. Pathogens, brainstorm to die once incorporated into garden soil, and research has shown that incorporating manure at least 120 days before harvest greatly reduces risks of food borne affliction.
Herbicide Residual
In that location have been many cases where vegetable gardeners have unknowingly used manure and composts that are contaminated with herbicides and have seen herbicide injury in their vegetable gardens. The herbicides of business concern are broadleaf herbicides used on lawns, turfgrass, pastures, and hay crops. Some of these materials tin can retain herbicidal activity for a long fourth dimension, even afterwards passing through an beast'due south digestive system, and fifty-fifty after the resulting manure is composted. Treated grass clippings, and compost fabricated from treated grasses, can also retain residues. The herbicides practise eventually breakup and lose activity over fourth dimension, specially as they are exposed to microbes, heat and moisture. This can take place relatively chop-chop, or can take upwards to several years, depending on the situation.
On sensitive crops, these herbicides tin can cause poor formation and kill seedlings, and they cause new leaves to get twisted and malformed. Sensitive crops include a broad array of crops including tomato plant and other solanaceous crops, lettuce, beans and other legumes, strawberries, grapes, and virtually other vegetable crops.
If y'all purchase manures and composts, brand sure to exist aware of this possibility and get assurance that herbicides are not nowadays.
To Minimize the Wellness Risks Associated with Using Manures in Dwelling house Gardens
- Wait at to the lowest degree 120 days afterward applying raw or aged manure to harvest crops that grow in or near the soil (root crops, leafy greens, strawberries). Wait at least 90 days for other crops.
- Once the garden is planted, avoid using animal manures unless they accept been pasteurized or actively composted.
- Never use cat, canis familiaris or pig manure in your compost pile or your vegetable garden. These manures are more likely to incorporate parasites that infect humans than other manures.
- Wash vegetables before eating.
- People who are specially susceptible to foodborne illnesses should avoid eating uncooked vegetables from manured gardens. Those who face special risks from foodborne illness include meaning women, very young children, and persons with chronic diseases.
In Conclusion
While manures and composts are excellent soil amendments for the domicile gardener, gardeners should exist enlightened of the potential environmental and health risks associated with using manures and manure-based composts. Regular soil testing can assist gardeners avoid soil phosphorus buildup from continuously applying manures and composts to soils, and gardeners can follow some simple tips to reduce the health risks associated with applying fresh manures to vegetable gardens.
Download the Resource for the complete fact sail and a printable version.
Source: https://extension.unh.edu/resource/guidelines-using-animal-manures-and-manure-based-composts-garden-fact-sheet
Posted by: brownefolisn.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Is Dried Animal Manure Used For?"
Post a Comment